Current issue
Online first
Archive
About the Journal
Aims and scope
Publisher and Editorial
Advertising policy
For Authors
Paper review procedures
Procedures protecting authentic authorship of papers
Paper preparation manual
Plagiarism check
Publication ethics
Reviewers
APC
Editorial and Scientific Board
Contact
Reviewers
CFD simulations and NEDC tests for the original and replacement selective catalytic reduction system
1
Instytut Techniki, Akademia Nauk Stosowanych, Poland
Submission date: 2024-11-29
Final revision date: 2025-02-23
Acceptance date: 2025-02-24
Online publication date: 2025-03-20
Corresponding author
Damian Kurzydym
Instytut Techniki, Akademia Nauk Stosowanych, Akademicka 1, 47-400, Racibórz, Poland
Instytut Techniki, Akademia Nauk Stosowanych, Akademicka 1, 47-400, Racibórz, Poland
KEYWORDS
TOPICS
ABSTRACT
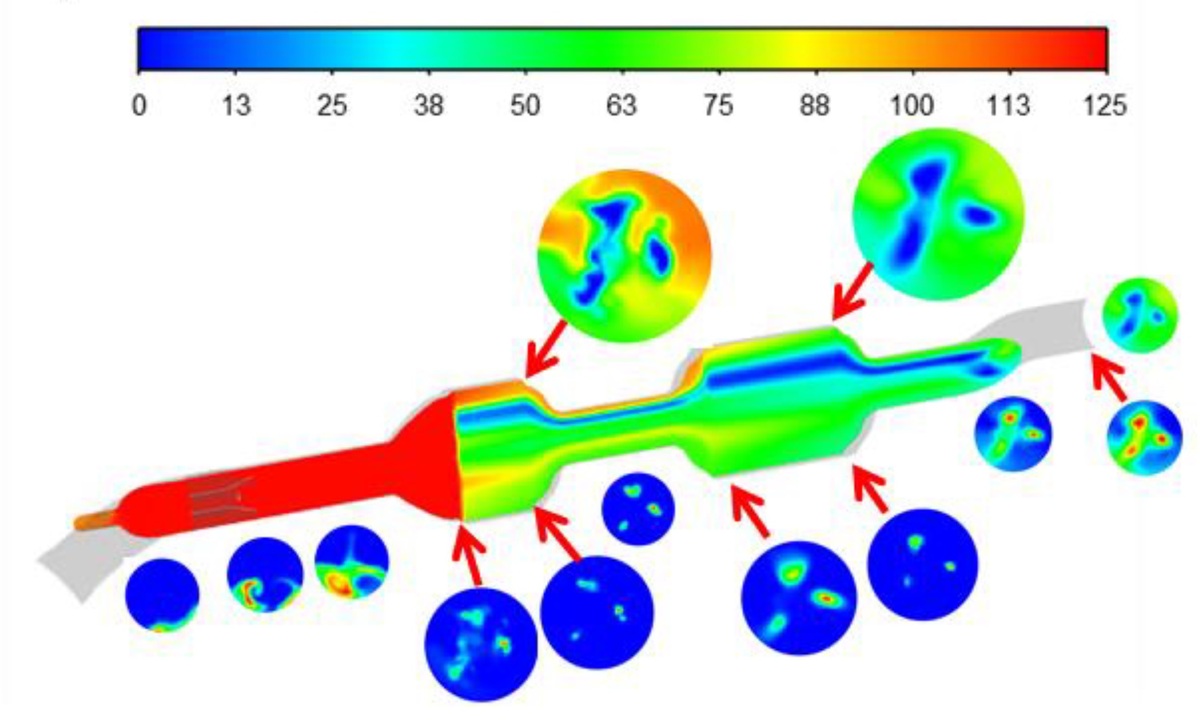
The purpose of this study was to perform both experimental and computational investigations on the selective catalytic reduction (SCR) system in passenger cars equipped with compression ignition (CI) engines. The study involves a comparison of results obtained for two separate SCR systems: an existing one and a newly developed system. The newly designed SCR system is intended for implementation in the spare parts market (Aftermarket) and includes the creation of a custom mixer design. This research analyzed multiple SCR systems and mixers under varying operating conditions. Various factors were considered, including the examination and evaluation of gas distribution and nitrogen oxide reduction. The multiphase computational fluid dynamics analyses were conducted using the ANSYS Fluent software. A detailed assessment was carried out for the sequential processes occurring within the system. The final version of the replacement SCR system was analyzed in relation to the original system supplied by the original equipment manufacturer (OEM). The implementation of the new mixer in the replacement SCR system led to slightly reduced NOX emissions, as validated by emission tests (NEDC) performed in a car on a chassis dynamometer within a certification unit.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The author of this article expresses gratitude to Tenneco for funding the research. Additional appreciation is extended to the State University of Applied Sciences in Racibórz for supporting participation in the VIII Young Scientists Academy conference and for funding the publication of this article.
REFERENCES (17)
1.
Brzeżański M. Diesel engines with respect to Euro 6 and BIN5/LEV II emission limits. J. KONES Powertrain and Transp. 2011;18(4):33-40. https://kones.eu/ep/2011/vol18....
2.
Dzida J, Brzeżański M. An analysis of SCR reactor deactivation impact on NOx emissions from a compression ignition engine. Combustion Engines. 2019;178(3):208-212. https://doi.org/10.19206/CE-20....
3.
Gis W, Grzelak P, Taubert S, Żółkowski A. Evolution of the effectiveness of replacement catalytic converters. Combustion Engines. 2013;154(3):569-574. https://bibliotekanauki.pl/art....
4.
Jansson J. Vanadia-based catalysts for mobile SCR. In Nova I, Tronconi E. (eds.), Urea-SCR technology for deNOx after treatment of diesel exhausts. Springer, New York 2014.
5.
Johnson TV. Review of selective catalytic reduction (SCR) and related technologies for mobile applications. In Nova I, Tronconi E. (Eds.), Urea-SCR technology for deNOx after treatment of diesel exhausts. Springer, New York 2014.
6.
Khajepour A, Fallah MS, Goodarzi A. Electric and hybrid vehicles: technologies, modeling and control – a mechatronic approach. Wiley-Blackwell 2014
7.
Kobayashi M, Kuma R, Masaki S, Sugishima N. TiO2-SiO2 and V2O5/TiO2-SiO2 catalyst: physico-chemical characteristics and catalytic behavior in selective catalytic reduction of NO by NH3. Applied Catalysis B: Env. 2005;60(3-4):173-179. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apca....
8.
Kröcher O. Chapter 9. Aspects of catalyst development for mobile urea – SCR systems – from vanadia-titania catalysts to metal-exchanged zeolites. Studies in Surface Science and Catalysis. 2007;171:261-289. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0167-....
9.
Kurzydym D, Klimanek A, Żmudka Z. Experimental research and CFD analysis of flow parameters in a SCR system for the original part and WALKER’s replacement. Combustion Engines. 2019;179(4):13-20. https://doi.org/10.19206/CE-20....
10.
Kurzydym D, Żmudka Z, Perrone D, Klimanek A. Experimental and numerical investigation of nitrogen oxides reduction in diesel engine selective catalytic reduction system. Fuel. 2021;313:122971. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel....
11.
Kuta K, Nadimi E, Przybyła G. Ammonia CI engine aftertreatment systems design and flow simulation. Combustion Engines. 2022;190(3):3-10. https://doi.org/10.19206/CE-14....
12.
Latha HS, Prakash KV, Veerangouda M, Maski D, Ramappa KT. A review on SCR system for NOx reduction in diesel engine. Int J Curr Microbiol App Sci. 2019;8(4):1553-1559. https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcma....
13.
Li J, He H, Hu C, Zhao J. The abatement of major pollutants in air and water by environmental catalysis. Front Environ Sci Eng. 2013;7(3):302-325. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11783....
14.
Liu X, Wu X, Xu T, Weng D, Si Z, Ran R. Effects of silica additive on the NH3‐SCR activity and thermal stability of a V2O5/WO3‐TiO2 catalyst. Chinese J of Catalysis. 2016;37(8):1340-1346. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1872-....
15.
Reşitoğlu İA, Altinişik K, Keskin, A. The pollutant emissions from diesel-engine vehicles and exhaust aftertreatment systems. Clean Techn Environ Policy. 2015;17:15-27. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10098....
16.
Schmidt H, Johannsen R. Examination of pollutants emitted by vehicles in operation and of emission relevant components – replacement catalytic converters. BASt. 2014.
17.
Yuan X, Liu H, Gao Y. Diesel engine SCR control: current development and future challenges. Emiss Control Sci Technol. 2015;1:121-133. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40825....
Share
RELATED ARTICLE
We process personal data collected when visiting the website. The function of obtaining information about users and their behavior is carried out by voluntarily entered information in forms and saving cookies in end devices. Data, including cookies, are used to provide services, improve the user experience and to analyze the traffic in accordance with the Privacy policy. Data are also collected and processed by Google Analytics tool (more).
You can change cookies settings in your browser. Restricted use of cookies in the browser configuration may affect some functionalities of the website.
You can change cookies settings in your browser. Restricted use of cookies in the browser configuration may affect some functionalities of the website.